The Pareto Criterion Tells Us Which Pareto-efficient Allocation Is Best
The Pareto criterion says that a move is efficiency enhancing only if at least one person gains from the move and no one loses and that a particular outcome is efficient if there is no move from that position which leaves each party at least as well off as they were in the original position. 11 Pareto-dominates T T.

Pareto Efficiency An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
1 be a Pareto allocation for the given utility functions and endowment x.
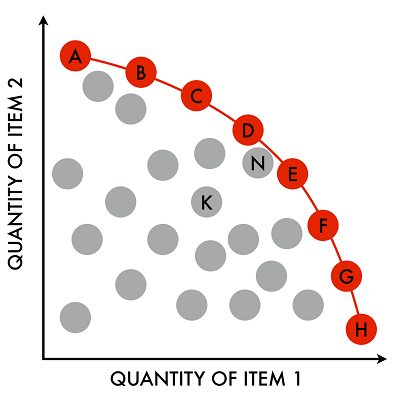
. In Pareto efficiency the resources are allocated in a most efficient manner possible most economically efficient way. In this case the Pareto criterion does not tell us which of the Pareto-efficient allocations is better It does not give us any ranking of efficient allocations Pareto efficiency has nothing to do with fairness efficient allocations are not necessarily fair. Pareto criterion tells us that 1 1 is the best outcome as it is Pareto-efficient.
Pareto efficiency or optimality is another way to measure efficiency. It does not give us any ranking of I I I T and T I. An allocation x XY say is Pareto e fficient or.
Anil playing IPC and Bala free riding by playing Terminator is Pareto efficient but we and Anil may think this is unfair. Since xbin 1 is a Pareto allocation it is a solution of the Pareto maximization problem P-max and it therefore satis es the rst-order marginal. If it is feasible and there exists not feasible allocation that is Pareto superior to it.
Pareto efficiency analysis uses individuals as the basis of evaluation. The concept is named after Vilfredo Pareto 18481923 Italian civil engineer and economist who used the concept in his studies of economic efficiency and. Allocation X is Pareto efficient if.
In this case any change to the allocation has to make one person worse off so by definition its Pareto efficient. Pareto optimal if there does not exist another feasible allocation y such that by moving from x to y someone is made better offwhilenooneismadeworseoff. As long as how much each of you ends up getting sums up to 100 the allocation is Pareto efficient even if you keep all 100 Martorana.
Hence it gives resources at best. Allocation X is a Pareto improvement over allocation Y if. An allocation of goods is Pareto optimal when there is no possibility of redistribution in a way where at least one individual would be better off while no other individual ends up worse off.
In Pareto efficiency the resources are allocated not as a need or space for improvement. Pareto-efficiency does not necessarily mean that we should approve of it. A definition can also be made in two steps.
When is an allocation a Pareto efficient allocation. 14 Pareto Efficiency contd XDefinition. The second condition for Pareto optimum requires that the available factors of production should be utilised in the production of products in such a manner that it is impossible to increase the output of open firm without a decrease in the output of another or to increase the output of both the goods by any.
At a Pareto-efficient allocation of inputs. Every agent prefers or is indifferent between her consumption bundle under X to her bundle under Y. Even though Pareto efficiency implies that the resources are allocated in the most efficient manner it doesnt imply fairness or equality of the allocation of the resources.
Developed by Vilfredo Pareto 1848 1923 Pareto efficient allocation of goods occur when no other possible allocation makes at least one individual better off without making anyone else worse off. 1 1 and 1 T are Pareto-efficient. This preview shows page 13 - 17 out of 60 pagespreview shows page 13 - 17 out of 60 pages.
In fact Pareto efficiency doesnt equate to equality or fairness. This also implies the Pareto criterion of public policy or the Pareto-efficient allocation of resources implying when one person is made better off. Pareto efficiency or Pareto optimality is a situation where no individual or preference criterion can be better off without making at least one individual or preference criterion worse off or without any loss thereof.
If no consumer is worse off in allocation a than in allocation b and there is at least one consumer who is better off in a than b. X is Pareto efficient. If Anil and Bala moving from TT to 1 1 there is Pareto-improvement as both farmers are better off.
The Optimum Allocation of Factors. This efficiency criterion was developed by Vilfredo Pareto in his book Manual of Political Economy 1906. Improves Efficiency and Minimizes Cost.
The Pareto criterion does not tell us which of the Pareto-efficient allocations is better. If an allocation is Pareto efficient this does not mean we should approve of it. Allocation A Pareto-dominates allocation B if at least one party would be better off with A than B and nobody would be worse off.
We rst show that the conclusion holds for x i n 1 bx 1 ie if each consumers initial bundle is xbi. It uses the best allocation method making the resources work at their best and optimum ultimately reducing the cost. -a change from situation A to B.
Hence it gives resources at best. The firms will have equal marginal rates of technical substitution. If an allocation is Pareto efficient this does not mean we should approve of it.
An allocation x is Pareto ine fficient if there does exist. According to the Pareto criterion a desirable attribute of an allocation is that it be Pareto-efficient. The MRTS of one firm is equal to WR while.
If for every agent allocation X is on a higher or at least the same indifference curve. Pareto Efficiency in Production.

Pareto Improvement Overview How It Works Benefits

Pareto Efficiency Simple Definition Example Statistics How To


No comments for "The Pareto Criterion Tells Us Which Pareto-efficient Allocation Is Best"
Post a Comment